Vivado IP Versioning
IP Versioning
Table 1 describes the scope and impact of changes captured in the different updates AMD may make to cores in the IP Portfolio.
- There are three Change Levels used to capture the changes to an IP and the resulting impact to the user. They are, in increasing order of potential impact: Revision, Minor, and Major. The Major, Minor and Revision fields are displayed at key points in the Vivado GUI. All changes to the IP are recorded in the 'Change Log' file associated with the IP.
Table 1 IP Versioning
| Change Level | User Action | Examples of Changes |
| Revision | No need to react | Add new device support Cosmetic GUI changes Move device support from Pre-Production to Production Extend parameter range Bug fix for unusable configurations (no working configuration changed) |
| Minor | May need to react | Reduction in parameter range Remove an optional port Add a memory-mapped register whose use is optional Increased resource usage |
| Major | Will need to react | Add a non-optional, non-static input port Rename a non-optional port (including case change if Verilog) Change a non-optional port's size Remove a non-optional port Change the interface standard Change or remove a memory-mapped register Behavior change for all configurations |
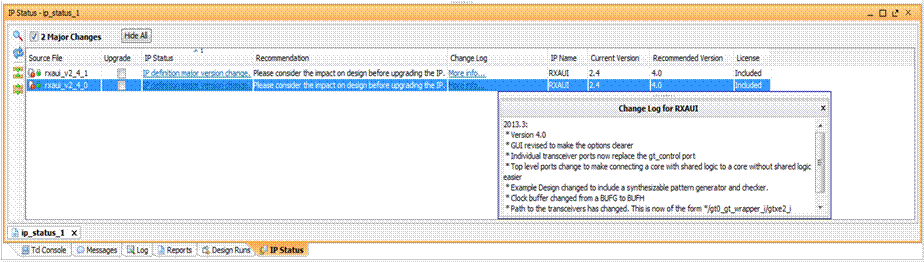
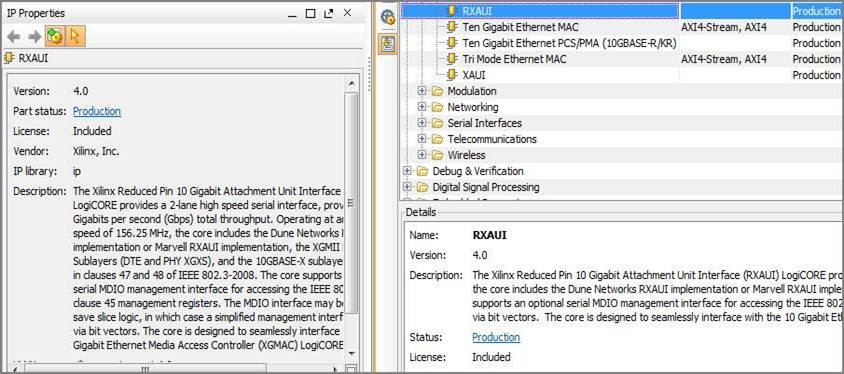
Figure 1: An example of IP version displayed in Vivado.
Locked IP & Upgraded of IPs:
Designs opened in a newer version of Vivado may have their IP locked. AMD recommends users to upgrade to the latest version of the IP, but user has a choice of upgrading the IP or remaining with the existing version of the IP. An IP may be locked because it is an older version and is no longer available in the catalog or is read-only due to the file system. If a locked IP has existing output products on disk they will be re-used by the flow. To make changes to the IP or to generate its output products it must be moved out of the locked state.
Moving an IP out of a locked state depends on the reason it is locked. For example, if the IP is an instance of an older IP the upgrade flow can be used to update the IP to the latest version. The Report IP Status window (available via the Tools>Report menu or via the report_ip_status Tcl command) will explain why the instances are locked and how to resolve the issues.
Figure 2 : A snapshot of the upgrade feature in Vivado.